What is bore water? (It is also known as Ground water and Well water)
Ground water is rainwater that seeps down through layers of soil and rock and settles in aquifers at different depths. Dams, creeks and rivers also contribute to groundwater supplies.
As the water permeates downwards it dissolves minerals from rocks and soil which affects the ground water hardness. The geology of the area determines the mineral make up, structure and content of the ground water supply. Groundwater may also be affected by hardness, salinity and other naturally occurring chemicals.
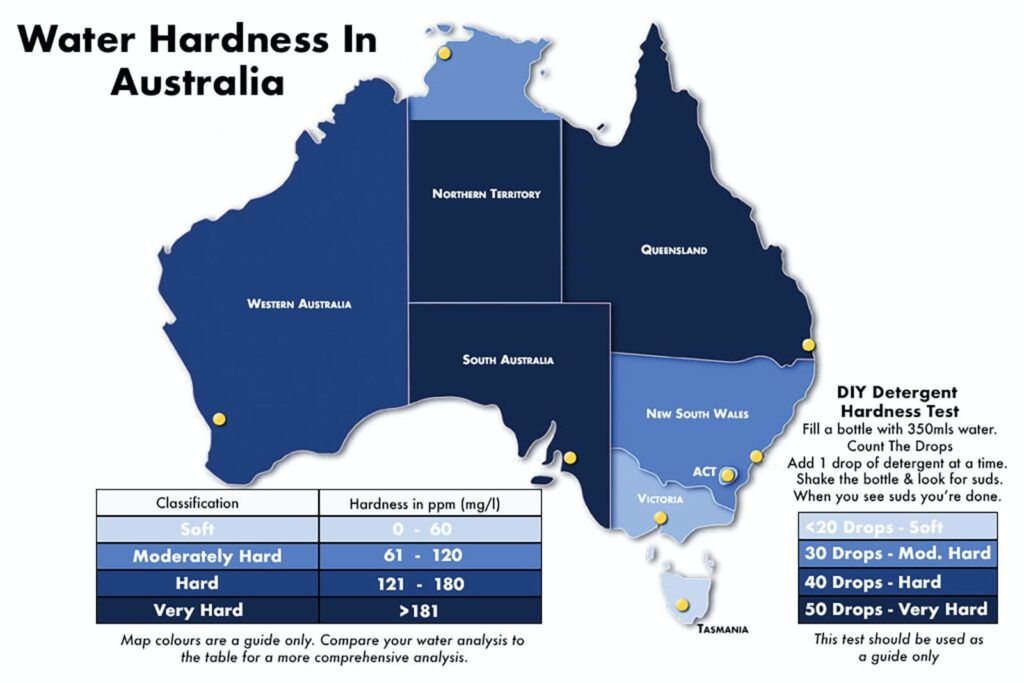
What are the most common minerals found in bore water?
Calcium and magnesium are the two most common minerals found in water that make water “hard.” The higher the calcium and magnesium concentration, the greater the hardness of the water and the greater the scaling problem.

Is bore water safe to use?
Water from bores is a valuable resource and can contribute significantly in meeting your water needs. Bore water may be fine for showering, food preparation and drinking. Depending on its quality it may only be used for stock watering, irrigation, flushing toilets and washing clothes or cars.
Ground water aquifers can become contaminated by natural processes and human activities. Before drinking your bore water, have it tested by an accredited laboratory to confirm the quality of the water is safe to drink.
Are there minerals in water?
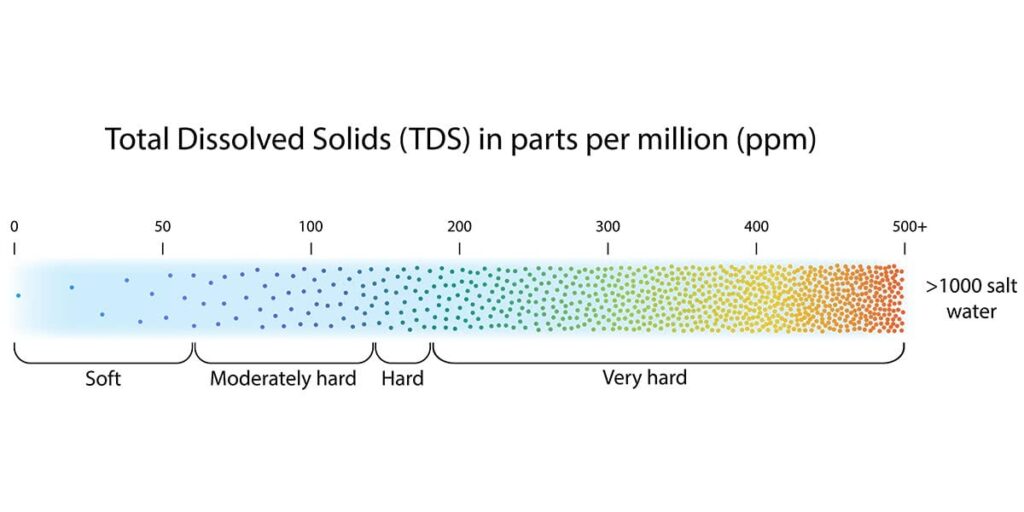
Yes, all water supplies and sources contains minerals no matter where you live in Australia or around the world.
The most common dissolved mineral substances are sodium, calcium, magnesium, potassium, chloride, bicarbonate, and some areas have iron. Water from some bores may contains very large concentrations of dissolved minerals making it not suitable for humans and animals to drink or to irrigating crops and plants.
Calcium and magnesium minerals deposit as a white hard crusty scale on sinks, taps, shower heads, shower screens and tiles, pipes, hot water heating elements or any surface that gets wet. Hard water problems in the home, caravan or RV are a nuisance. The amount of minerals in water affects the amount of soap and detergent necessary for cleaning. Bathing with soap in hard water leaves a film of sticky soap curd on the skin that irritates skin conditions like eczema and dermatitis. Shampoo and conditioner on hair may make it dull, lifeless, frizzy, difficult to manage and hard to rinse out.
When doing laundry in hard water, soap suds lodge in fabric during washing to make fabric stiff and rough. Ineffective washing and rinse cycles causes greying of white fabric and the loss of brightness in colours shortening the life of clothes. In addition, soap curds can deposit on dishes, bathtubs and showers, and all water fixtures.
Hard water also contributes to inefficient and costly operation of hot water systems and appliances like dishwashers, washing machines, kettles and coffee machines. When water is heated it builds up on heating elements forming calcium and magnesium scale. To heat the water, you first need to heat the scale. As the scale thickens around the heating element hot spots develop and the element fails. Pipes can become clogged with scale that reduces water flow and ultimately requires pipe replacement.
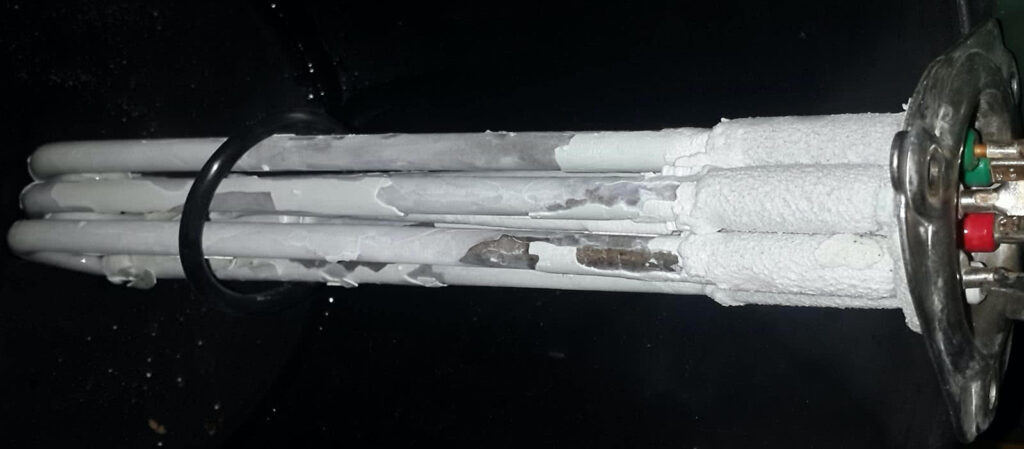

The Clean Water Co supply a range of Softerwater conditioners that are chemical and slat free, have no moving parts or replacement parts and protect your plumbing fittings and appliances from hard water problems. We can supply a Softerwater conditioner for whole of house, sh
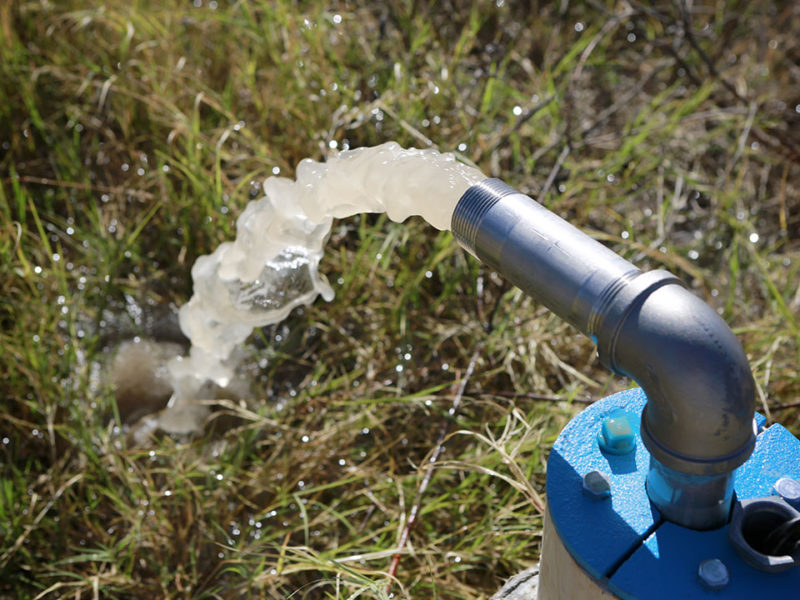

 Minerals in water
Minerals in water

