It is common practice to install filters in the following sequence
Option 1 | Two Stage Filtration
- Sediment filter
- High flow powder activated carbon & silver impregnated low micron filter
Option 2 | Two Stage Filtration
- 5 Micron carbon filter
- High flow powder activated carbon & silver impregnated low micron filter
At The Clean Water Co we know that filters remove sediment, chemicals and bacteria but do nothing to prevent problems with hard water scaling or soft water corrosion. We offer alternative water treatment solutions including filtration, scale and corrosion protection as well as UV disinfection.
Terms commonly used when discussing water filtration
If you’re considering a water filtration system, you’ve probably come across a number of industry related terms. Here, in simple language, is what each of these industry terms mean and why they are important when selecting a water filtration system:
pH
pH measures the level of hydrogen ion concentration in your water and refers to the water’s acidity or alkalinity. The pH scale usually ranges from 0 to 14. Aqueous solutions at 25°C with a pH less than 7 are acidic, while those with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline.
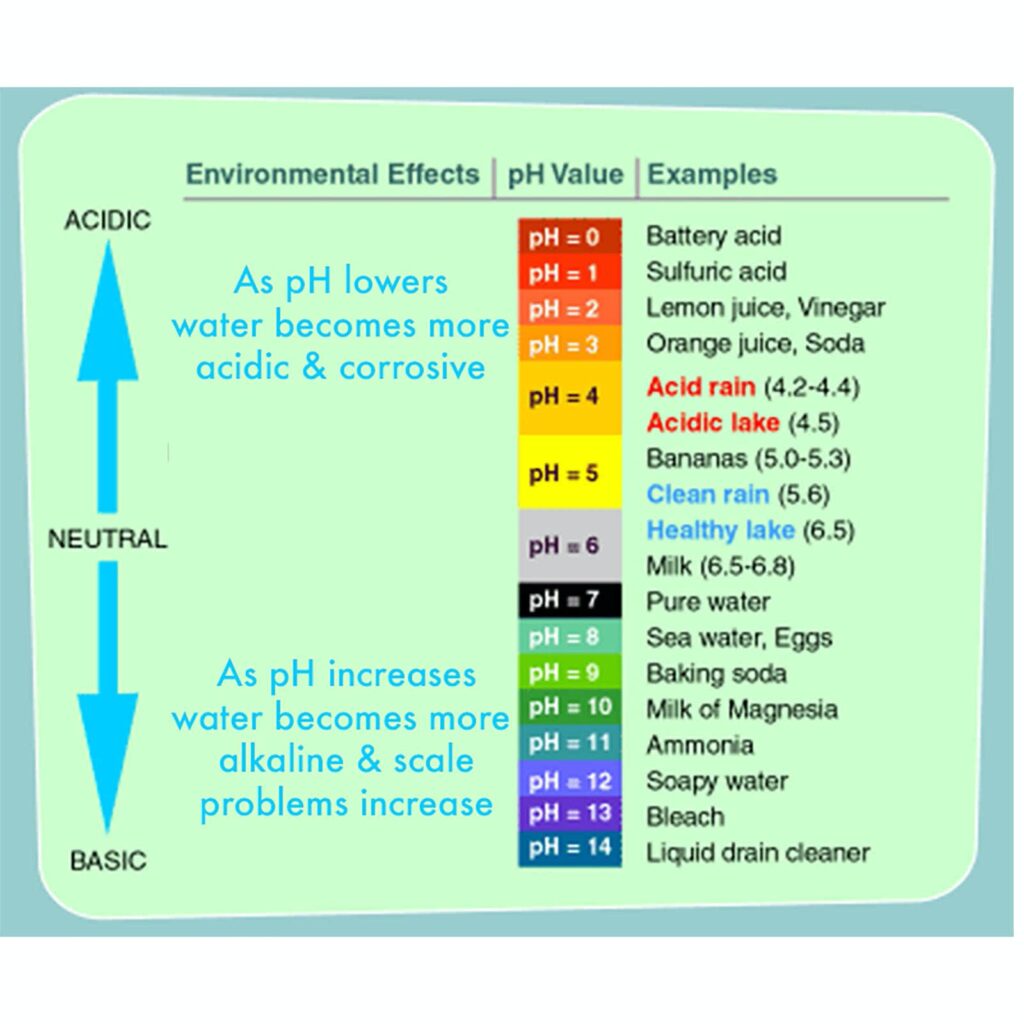
There’s a lot of debate about what pH level is best, especially when it comes to drinking water. But it’s not just your drinking water that is affected by the pH level. For example, a low pH level in your water is acidic and will corrode taps and fittings. Extremely acidic water can leach copper from your pipes and create a problem called Blue Water Syndrome.
You might think the solution is to keep the pH level in your water high. But a high pH level brings its own problems. High pH water is more alkaline and can cause scale to form in your pipes taps and fittings, as well as on heating elements, shower heads and shower screens.
Micron rating
The micron rating measures the distance between pieces of filtration media and determines the size of particles that the filter will allow to pass through. Typically, the smaller the micron rating the better the filter. Think of it like a tunnel on a highway. The larger the vehicle that uses the tunnel, the wider the mouth of the tunnel needs to be. To stop these large vehicles, engineers simply make the mouth and height of the tunnel smaller to prevent the large vehicles from entering. Same goes for water filtration systems.
The average cross-section of a human hair is 50 microns and the human eye cannot see anything smaller than 40 microns in size.

Now, protozoa such as Giardia and Cryptosporidium are about 5 microns in size and bacteria such as Cholera, E. Coli, and Salmonella are even smaller (0.2 – 0.5 microns) and viruses such as Hepatitis A, are about 004 microns. Most filters won’t filter out these bacteria and microbes unless UV or other treatment is applied.
Totally dissolved solids (TDS)
When we talk about TDS or total dissolved solids, we’re talking about the concentration of dissolved substances in your water. TDS come in the form of inorganic salts and a small amount of organic matter. Calcium, magnesium, potassium and sodium are all examples of common inorganic salts called cations and are ions with a positive charge. Carbonates, nitrates, bicarbonates, chlorides and sulphates are TDS,s classified as anions and have a negative charge.
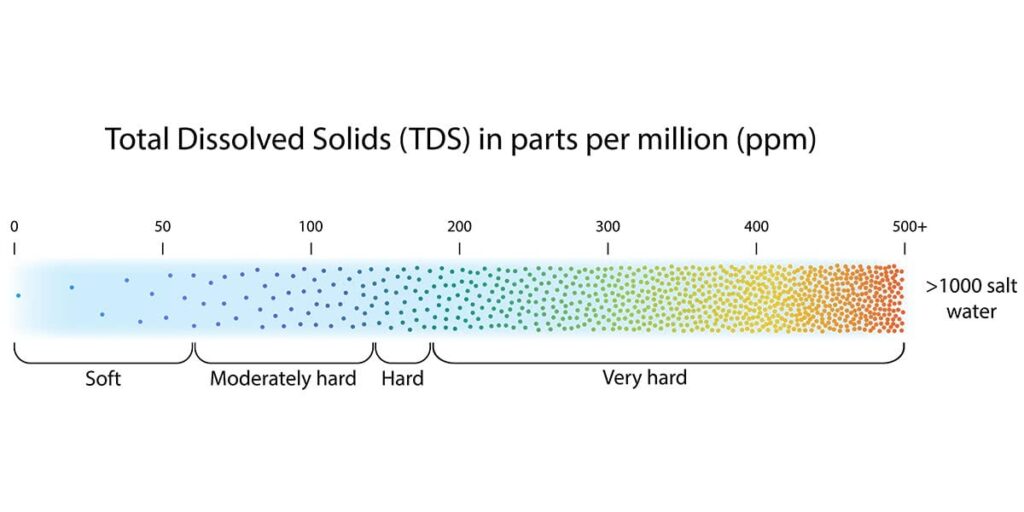
These minerals, classified as anions and cations originate from a number of sources, both natural and as a result of human activities. For example, a mineral spring containing water that has passed through a region with high rock salt content will have a high level of dissolved solids collected from the rocks.
Water from agricultural and urban runoff tends to contain excess minerals, as can wastewater discharges and industrial wastewater.
UV disinfection
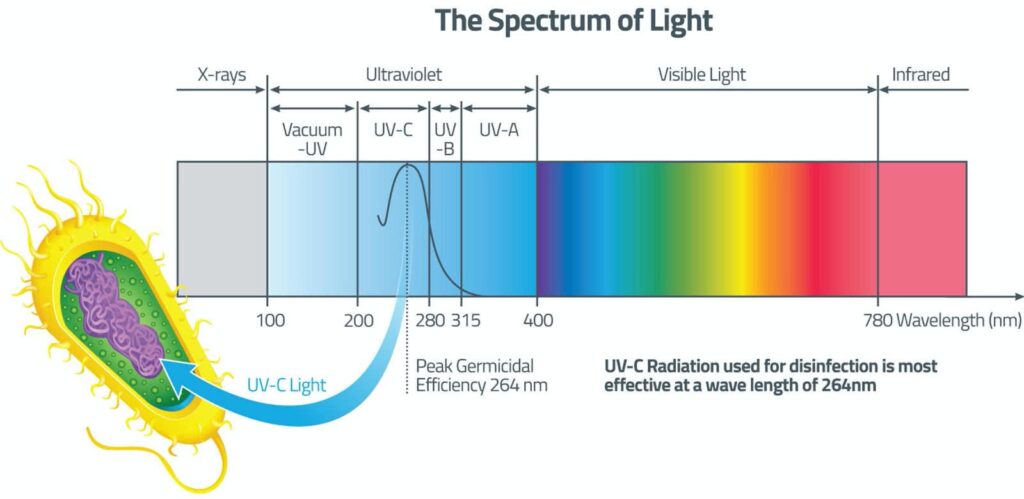
Alternatively you can install a UV disinfection system or Ultra-Violet light which either destroys microorganism on contact or stops their ability to reproduce. The optimum UV wavelength for UV disinfection is 264 nanometers within the UV-C spectrum. But a germicidal wavelength range between 200 and 300 nanometers is suitable in many instances. How it works: When the UV light comes in contact with viruses, spores or bacteria breeding in your water supply absorb the UV rays into the DNA rendering them incapable of reproduction or infection.
A UV dose of 40 mJ/cm² (400 J/m²) will give a 99.9% reduction in almost all human pathogens swimming around in your drinking water.
Sediment filters
As the name suggests, a sediment filter filters out sediment in your water. By sediments I mean the visible particles such as dirt, sand, dust, rust or organic compounds present in your water supply. Low micro sediment filters can also also remove the cloudiness in water caused by suspended solids, giving your water that crystal-clear look that makes water look and feel so refreshing. Sediment filters have a micron rating. The lower the micron rating the more particles the filter will remove and the more sparkling your water will be.
Carbon filters
If your water has a chlorine taste or strong odour, then you likely need a carbon filter. Carbon filters have a carbon cartridge that needs to be replaced roughly every 12 months, depending on volume of use, and are most effective at removing chlorine, and something we call volatile organic compounds (or VOC’s for short) as well as improve taste and odour from your water. Although carbon filters vary, a typical carbon filter will have a micron rating in the range of 0.5 to 50 microns.
If you know for a fact that you have heavy metals such as lead in your drinking water, you need a 0.5 micron rated carbon block filter. Keep in mind, a 0.5 carbon filter could reduce the pressure and flow rate from your tap as more pressure is required to force the water through the carbon block filter. However, the possibly lower flow rate is worth it for a better-quality drinking water.
Silver impregnated carbon filters
Activated carbon filters trap organic substances. Trapped organic substances create a breeding ground for microbial flora, which is not good. The solution is to use a Bacteriostatic silver activated carbon to inhibit the growth of microbiological matter and biofilms trapped inside the carbon water filter.
That’s where carbon filters impregnated with silver come in. Silver is proven to prevent the growth of ash or dust fed bacteria that becomes trapped in the carbon filter. Silver occurs naturally in the soil. And because silver ions stop bacteria from forming, silver is often used as an emergency disinfectant in drinking water. Silver is also used in some water filters to provide drinking water that is safe from microbial regrowth.
This is especially important when using rainwater. If you use rainwater you should use a bacteriostatic carbon filter to avoid the risk of waterborne illnesses that can result from bacteria that forms in activated carbon filter.
Hard vs soft water
Water hardness varies across Australia. For example, Hobart’s water is considered very soft at just 10 mg/L. Sydney’s water is also soft, at a hardness level of about 50mg/L. Brisbane and Adelaide, on the other hand, have water with a very high hardness rating of around 90-100 mg/L. On a state level, you’ll find the hardest water in Western Australia and South Australia. And the softest water in Victoria and Tasmania.
Soft water normally has a lower pH or more acidic water which is prone to causing corrosion problems with pipes, taps, faucets, shower heads and other plumbing fittings. Installing a home water filter combined with the appropriate mineral conditioner combats the problems with both hard and soft water and keeps your family safe from the bacteria and protozoa that breed in our water system.

 Tank water supplies
Tank water supplies

